
Specialized types are used for high voltage switches, for radio-frequency amplifiers, or for switching high currents. These transistors are current regulating devices that control the amount of current flowing from an emitter to collector terminals in proportion to the amount of biasing voltage.

Bipolar transistors are still used for amplification of signals, switching, and in mixed-signal integrated circuits using BiCMOS. Bipolar Transistor is a type of transistor that uses electrons as well as holes as charging carriers. Hundreds of bipolar junction transistors can be made in one circuit at very low cost.īipolar transistor integrated circuits were the main active devices of a generation of mainframe and minicomputers, but most computer systems now use CMOS integrated circuits relying on field-effect transistors. Diffused transistors, along with other components, are elements of integrated circuits for analog and digital functions. Different metal work-function electrodes are used to induce n- and p-type charge. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Bipolar Charge Plasma Transistor (BCPT) is explored using 2-D simulations. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. (Source: ©tilialucida - ) A bipolar junction transistor, also called bipolar transistor, is a three-terminal device that can function as electronic switch or signal amplifier. In contrast, the saturation and cut-off regions allow bipolar transistors to be used as switches because there is little electrical resistance between emitter and collector in the saturation region and little current flows in the cut-off region.BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. A bipolar junction transistor (bipolar transistor or BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and holes as charge carriers. Therefore, an amplifier circuit can be configured using the active area. When a bipolar transistor is in the active region, the collector current is basically h FE times the base current.
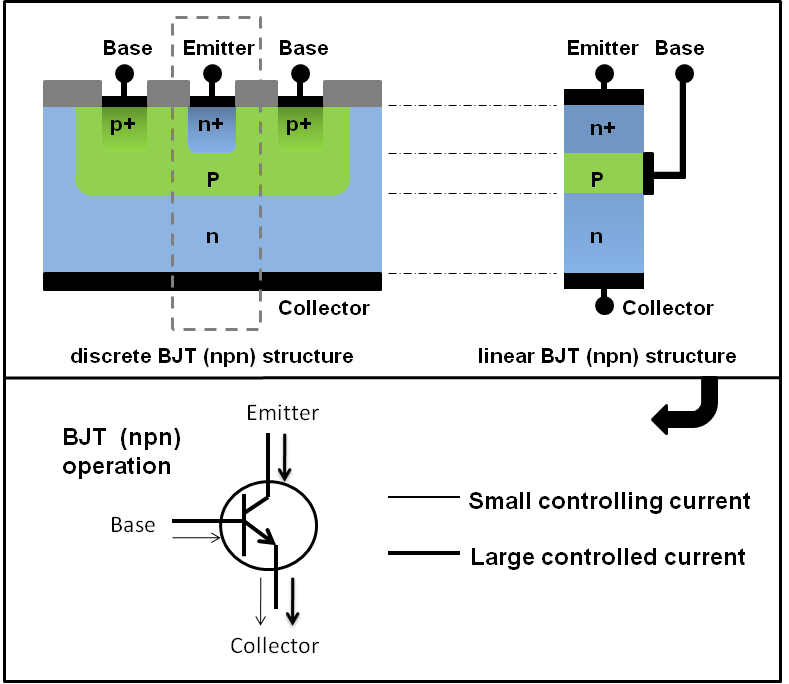
Unlike a normal p-n junction diode, this transistor has two p-n junctions. It is solid state device that flows current in two terminals, i.e., collector and emitter and controlled by third device known as terminal or base terminal.

Therefore, if the emitter and collector terminals are reversed, a bipolar transistor has a much lower h FE and does not function as intended. A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is a three terminal circuit or device that amplifies flow of current. (For example, in the case of an npn transistor, the collector and the emitter on both sides of the p region of the base are n regions, which look the same.) However, the dopant concentrations in the collector and emitter regions are quite different. The structure of a bipolar transistor looks symmetrical. Two types of bipolar transistor are available, known as npn and pnp, based on the type of junction. Since the bipolar transistor was the first transistor to be invented, when one simply says "transistors," it sometimes means bipolar transistors.
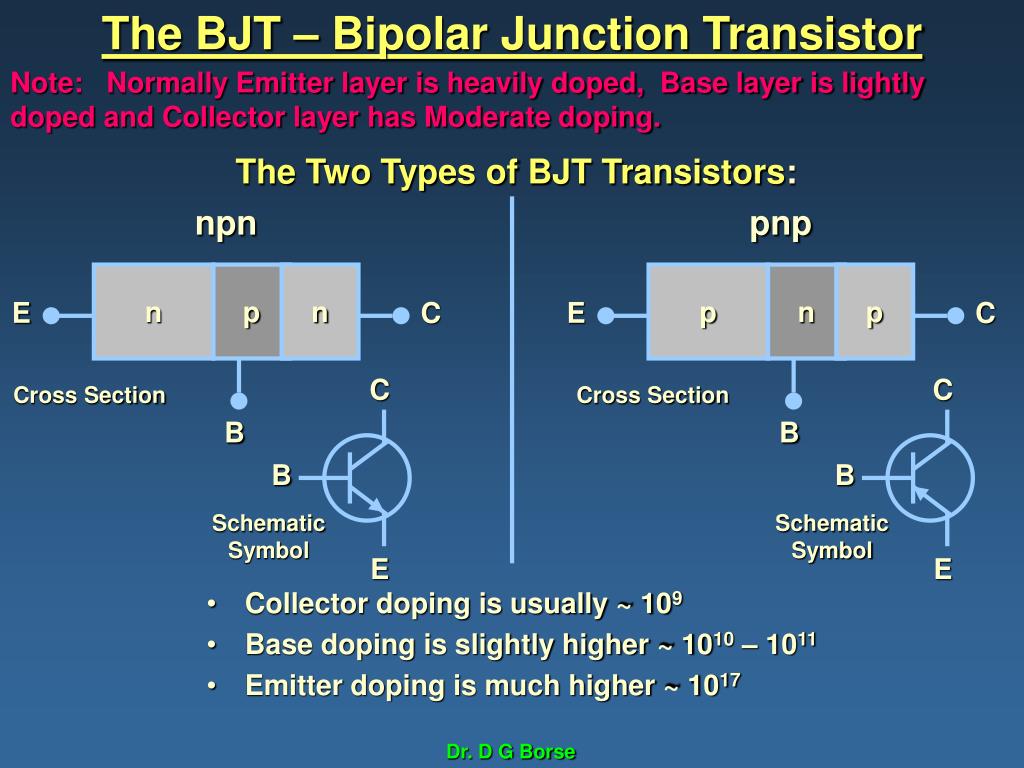
Whereas a field-effect transistor is a unipolar device, a bipolar transistor is so named because its operation involves two kinds of charge carriers, holes and electrons. Nexperias low power loss, fast bipolar families of high-voltage transistors are ideally suited to high frequency switching in any powered application. These three terminals are known and labelled as the Emitter ( E ), the Base ( B ) and the Collector ( C ) respectively. Bipolar transistors are a type of transistor composed of pn junctions, which are also called bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). RF bipolar transistors with different voltage classes, frequency ranges, and output power, are available and based on Infineons vast microwave bipolar. The Bipolar Transistor basic construction consists of two PN-junctions producing three connecting terminals with each terminal being given a name to identify it from the other two.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
